ENDOSCOPY
TIPES OF ENDOSCOPIES
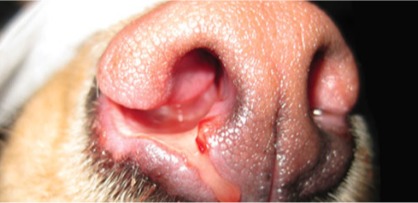
Rhinoscopy not only allows us to see the different nasal horns but will also allow us to take samples for biopsy, culture and antibiogram and also to perform washes if necessary.
Veterinary Rhinoscopy: When is it indicated?
Rhinoscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic technique that allows detailed exploration of the nasal cavities. It is especially indicated in the following cases:
-
Chronic nasal discharge, unilateral or bilateral
-
Chronic or recurrent sneezing
-
Acute sneezing (suspected foreign body)
-
Deformation of the nasal bridge
-
Epistaxis (nasal bleeding), unilateral or bilateral
-
Nasal pain or hypersensitivity
-
Nasal stridor (abnormal breathing sound)
-
Ulcers on the nose
-
Intense or persistent reverse sneezing
It is also recommended when suspecting:
-
Bacterial, fungal, or parasitic rhinitis
-
Nasal polyps
-
Neoplasms (tumors)
-
Other structural abnormalities of the upper respiratory tract
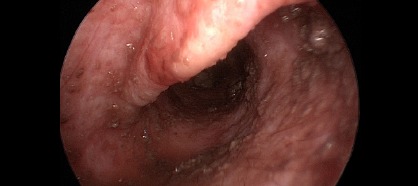
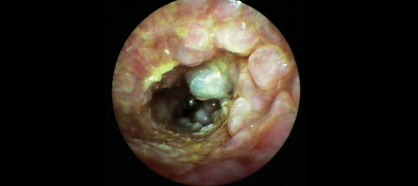
Veterinary video-otoscopy: when is it indicated?
Video-otoscopy is an advanced technique that allows detailed exploration of the ear canal and tympanic membrane with high-quality imaging and magnification. It is especially recommended in the following cases:
-
Chronic and recurrent external otitis
-
Middle ear otitis (inflammation of the middle ear)
-
When the tympanic membrane cannot be properly visualized during a routine examination
-
Presence of foreign bodies or masses inside the ear canal
-
Suspected nasopharyngeal polyps in cats or Horner’s syndrome
-
Deep ear cleaning under general anesthesia, when there is a large accumulation of discharge and topical treatment needs to be initiated effectively, taking advantage of a full tympanic evaluation
Advantages of video-otoscopy over conventional otoscopy:
-
Greater magnification capacity, allowing detailed visualization of internal structures
-
Better illumination of the surgical or diagnostic field
-
Use of instruments such as forceps and catheters through the endoscope working channel
-
Option to record in digital format, useful for clinical follow-up or sharing with the owner
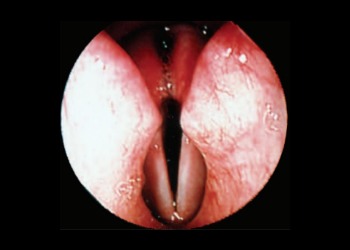
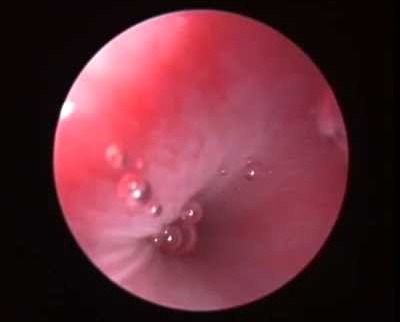
Veterinary Laryngoscopy: When is it indicated?
Laryngoscopy is an endoscopic technique that allows direct visualization of the larynx and upper airways. It’s essential for diagnosing respiratory problems and structural abnormalities.
Most common indications:
-
Stridor or upper airway noise
-
Exercise intolerance or unusual fatigue
-
Respiratory distress
-
Increased inspiratory effort or prolonged inspiration time
-
Changes in vocalization or barking
-
Coughing during eating or drinking
-
Veterinary Urethroscopy: When is it indicated?
Urethroscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure that allows visualization of the urethra and urinary bladder using an endoscopic camera. It can only be performed on females, due to anatomical limitations.
Most common indications:
-
Pollakiuria (increased frequency of urination)
-
Recurrent or chronic urinary tract infections
-
Persistent hematuria (blood in the urine)
-
Dysuria / Stranguria (pain or difficulty urinating)
This examination helps identify abnormalities such as tumors, foreign bodies, urethral strictures, or chronic inflammations that are often missed in standard tests.
-
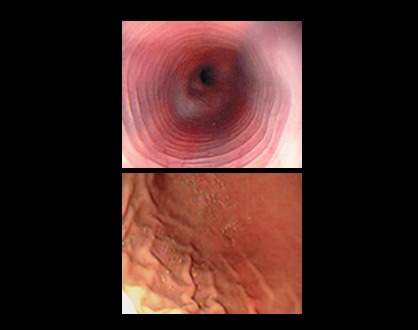
Video endoscopy allows us to visualize the state of the esophageal, gastric and early duodenal mucosa. However in small animals and some cats the duodenum may not be visible due to the size of the video endoscopy. Apart from seeing the structures, it will allow us to take samples by biopsy and to be able to reach a better diagnosis or the extraction of foreign bodies without the need to perform invasive surgeries.
Veterinary Gastroduodenoscopy: When is it indicated?
Gastroduodenoscopy is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure that allows direct visualization of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum, helping to diagnose gastrointestinal disorders effectively.
Main indications (in patients showing signs of digestive issues):
-
Nausea and ptyalism (excessive salivation)
-
Vomiting or hematemesis (vomiting blood)
-
Diarrhea or melena (black or tarry stools)
-
Loss of appetite or anorexia
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Persistent abdominal pain
Before performing a gastroduodenoscopy, a prior diagnostic protocol is recommended:
-
Complete blood count and biochemistry
-
Fecal analysis
-
Abdominal X-ray or ultrasound
-
Folate and cobalamin levels
-
Pancreatic tests: cPLI / fPLI
-
Empirical gastroenteric treatment and dietary modification
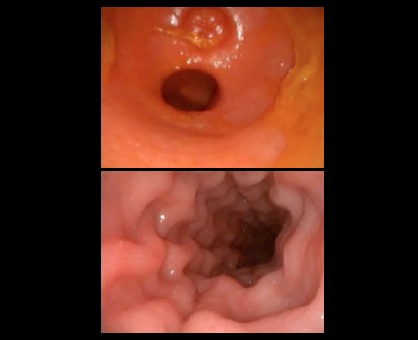
Colonoscopy: When is it indicated?
Colonoscopy is recommended for patients presenting the following symptoms:
-
Vomiting
-
Diarrhea / Melena / Hematochezia
-
Tenesmus / Flatulence
-
Loss of appetite / Anorexia
-
Weight loss
-
Abdominal pain
Before performing a colonoscopy, it is advisable to complete a prior diagnostic protocol, including:
-
Complete blood count and biochemical profile
-
Coprological analysis
-
Abdominal radiographs and ultrasound
-
Folate and cobalamin levels
-
cPLI and fPLI tests
-
Empirical gastrointestinal treatment and dietary adjustments
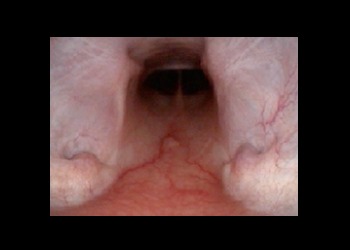
NASOPHARYNGOSCOPY
Nasopharyngoscopy is an endoscopic technique that complements rhinoscopy, allowing examination of the nasopharyngeal region to detect upper respiratory tract issues.
Common indications:
-
Frequent reverse sneezing
-
Inspiratory nasal wheezing
-
Nasal inspiratory stridor
-
Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)